Working with GitHub requires a secure way to connect and manage your repositories, but GitHub will no longer support password authentication after August 13, 2021. Instead, using SSH keys for authentication seems to be a better practice. In this blog post, I’ll walk you through the process of setting up SSH keys, adding them to GitHub and so on.
What Are SSH Keys?
SSH keys are a pair of cryptographic keys used to authenticate your identity when connecting to remote servers or services like GitHub. They consist of a public key, which you can share with others (or services), and a private key, which should be kept secret. When you connect to a server, your private key generates a signature that the server checks using your public key to verify your identity.
Step-by-Step Guide to Setting Up SSH Keys on Windows
Step 1: Generate the SSH Key Pair
Open your terminal (PowerShell or Git Bash) and run the following command:
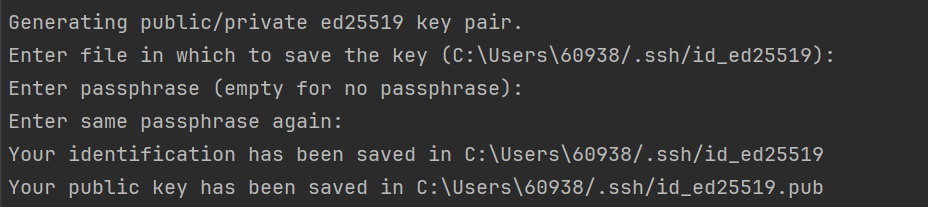
ssh-keygen -t ed25519 -C "your_email@example.com"
You’ll be asked where to save the key. Press Enter to accept the default location. If you want to add a passphrase for extra security, you can do so; otherwise, just leave it blank (Recommend).
Step 2: Start the SSH Agent and Add Your SSH Key to the Agent
To manage your SSH keys automatically, you need to start the SSH agent:
You should open the Git Bash (not the terminal in IDE or PowerShell), and then run the following command:
eval "$(ssh-agent -s)"
ssh-add ~/.ssh/id_ed25519
Step 3: Add Your SSH Key to GitHub
-
Copy your public key to the clipboard:
cat ~/.ssh/id_ed25519.pub -
Go to your GitHub SSH settings and New your SSH key.
Step 4: Test Your SSH Connection
Finally, let’s make sure everything is set up correctly. Run the following command (In the IDE terminal is OK) to test the connection:
ssh -T git@github.com
Follow the prompt and you will see the message showing the connection is successful.
